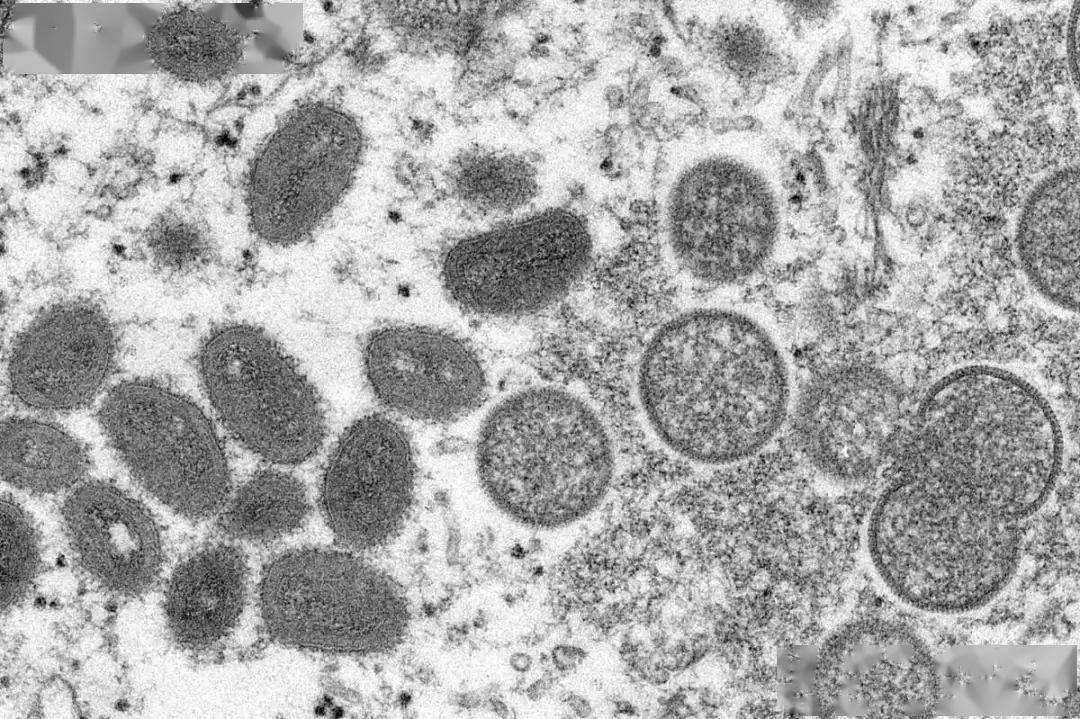
On July 12, WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus stated that there are now 9,200 cases of monkeypox in 63 countries around the world. WHO recommends that governments implement epidemiological investigations to help trace, contain the virus and isolate infected people, making sure to stop the spread of monkeypox.
Earlier, according to the National Broadcasting Corporation of the United States, as of July 8, there have been more than 700 confirmed cases of monkeypox in the United States, of which California and New York have the most. The epidemic is spreading like a snowball.
The U.S. government has ramped up monkeypox testing and vaccine distribution in recent days in response to rising cases. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services said in a statement on the 7th that it will distribute 144,000 doses of vaccines approved for monkeypox and smallpox viruses starting on the 11th. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention announced on the 6th that LabCorp, an independent medical laboratory in the United States, has opened a laboratory in North Carolina to conduct monkeypox tests with a testing capacity of about 10,000 tests per week. Four more commercial labs will also be operational in the coming weeks.