On September 12, Mersana announced that its ADC product XMT-1660 targeting was granted Fast Track designation by the FDA for the treatment of adult patients with advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
TNBC is the most aggressive type of breast cancer with the worst prognosis, accounting for about 15% of all breast cancers. TNBC cells lack estrogen receptors (ER) and progesterone receptors (PR), and only have limited human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), so effective treatment options are extremely limited. The mean time to metastases to recurrence in TNBC was approximately 2.6 years, compared with 5 years for other breast cancers. Among women with metastatic TNBC, the 5-year survival rate was 12%, compared with 28% for other types of metastatic breast cancer.
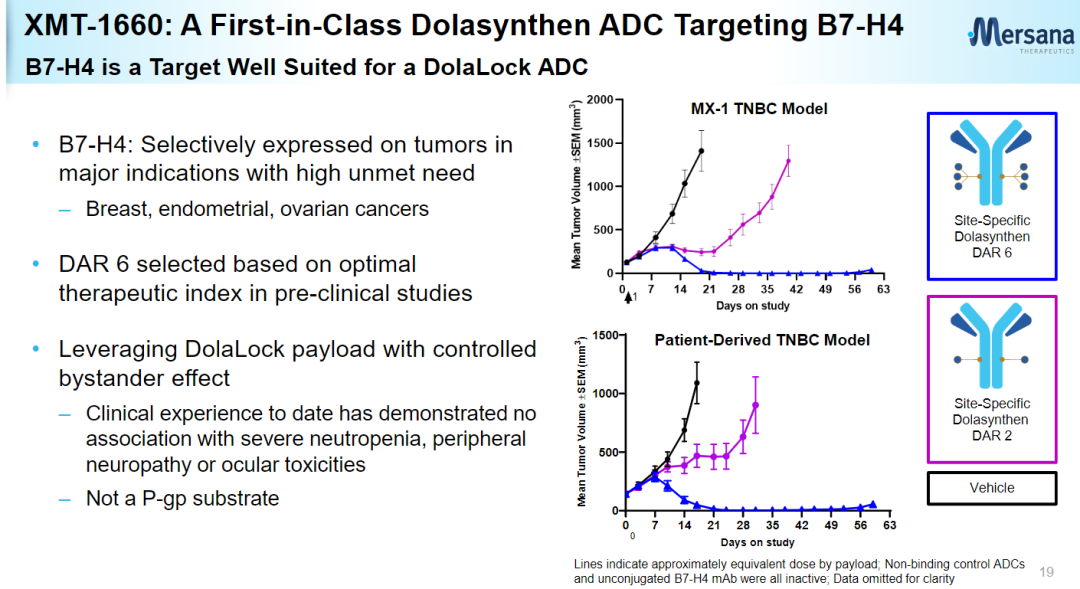
XMT-1660 is a B7-H4-targeted antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) developed using the Dolasynthen technology platform with a drug-to-antibody ratio of 6 (DAR=6), and is currently undergoing Phase I clinical trials. NCT05377996 is a multicenter dose-escalation and expansion Phase Ib study planned to enroll 166 patients including breast, endometrial, ovarian, fallopian tube and primary abdominal cancers to investigate the efficacy of XMT-1660 in solid tumors Safety, tolerability and antitumor activity in patients.
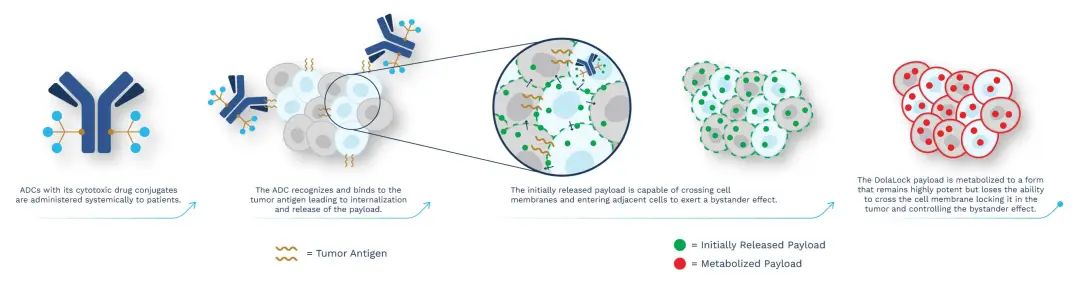
The Dolasynthen technology platform uses a tubulin inhibitor designed with Mersana’s proprietary DolaLock technology as a payload to generate homogeneous ADCs targeting specific sites. The payload spreads throughout the tumor within a short period of time and becomes locked within tumor cells, and if it spreads through adjacent tissues to normal cells, it is metabolized into a drug form that is still highly potent but no longer able to penetrate the cell membrane, resulting in a safe Controlled bystander effect. The properties of ADCs obtained through this platform are precisely balanced for optimal water solubility, charge balance, linker stability, and DAR, along with the advantages of Dolaflexin ADC technology.
Anna Protopapas, President and CEO of Mersana, said: “Breast cancer remains an area of high unmet clinical need, especially TNBC with particularly poor clinical outcomes and very limited treatment options. XMT-1660 shows promise in preclinical studies We are pleased to have recently initiated a Phase I trial of XMT-1660 to evaluate its safety and clinical activity. We are committed to bringing new therapies to the many cancer patients with B7-H4 expression, and this Fast Track designation It will likely expedite the FDA’s regulatory review of XMT-1660.”
At present, there are 5 drugs in the Mersana pipeline, among which upifitamab rilsodotin (UpRi) is the most advanced, and phase III studies are being carried out for high-grade serous ovarian cancer, fallopian tube cancer and primary peritoneal cancer.
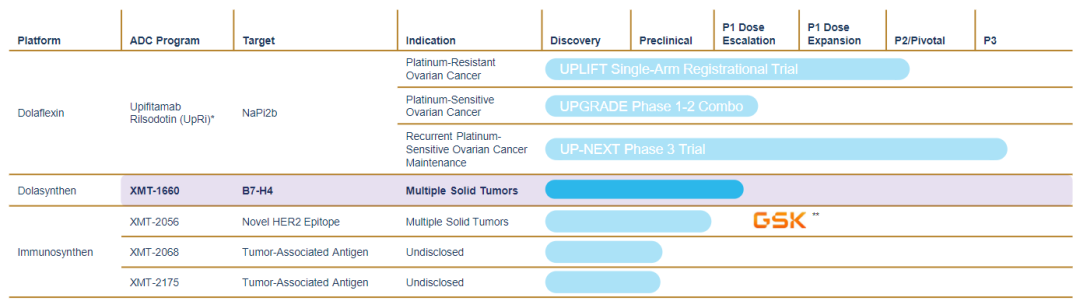
UpRi is a novel highly active sodium-dependent phosphate transporter 2B (NaPi-2b) antibody-drug conjugate developed using the Dolaflexin ADC technology platform, with an average of 15 auristatin F-hydroxypropylamide (AF-HPA) linked molecular. NaPi2b, a transmembrane sodium phosphate transporter encoded by the SLC34A2 gene, is expressed in both tumor and normal tissues. AF-HPA is a cell-permeable anti-mitotic compound that is slowly metabolized within tumors to the extremely low-permeable active metabolite auristatin F (AF), thereby controlling bystander killing effects.
Dolaflexin ADC technology utilizes Mersana’s proprietary Fleximer polymer, a biodegradable, highly biocompatible, water-soluble polymer capable of carrying a wide variety of drug molecules. In particular, the drug molecule is not directly bound to the antibody, but is first attached to the Fleximer backbone through an optimized, cleavable linker, and then bound to the antibody through a non-cleavable linker. Fleximer significantly improves drug solubility, pharmacokinetic properties, and immunogenicity, and significantly increases the number of drug molecules carried per ADC.
In addition, in addition to Mersana, some well-known pharmaceutical companies have also deployed B7-H4 targeted drugs. Among them, Hansoh Pharmaceutical, AstraZeneca and Seagen mainly develop B7-H4 ADC, and Pfizer, Genmab and Hebo Pharmaceutical mainly develop B7-H4 Double antibodies, NextCure and Five Prime Therapeutics (a subsidiary of Amgen) are mainly developing B7-H4 mAbs.
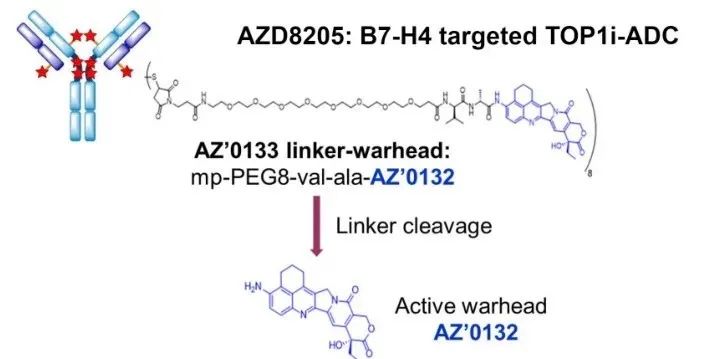
AZD8205 is composed of a novel topoisomerase 1 inhibitor (AZ’0132), a linker and a B7-H4 targeting antibody, and its mechanism of action is to deliver AZ’0132 into B7-H4 positive cells, resulting in DNA damage and cell death. In a study of 26 human TNBC PDX tumors, patients in the AZD8205 arm (IV, 3.5 mg/kg) achieved an overall response rate of 69% (30% or greater tumor regression from baseline), including The proportion of patients was 36% (9/26).
GEN1047 is a CD3/B7-H4-targeting bispecific antibody designed using the DuoBody platform, and is undergoing Phase I/II studies in malignant solid tumors. The DuoBody platform is a platform technology developed by Genmab after in-depth research on the unique mechanism of IgG4 antibody Fab arm exchange in the human immune system, which can stably produce bispecific IgG1 antibodies.